Surface of Asteroid Vesta
These two maps are derived from images of asteroid 4 Vesta taken between November 28 and December 1, 1994 with the Wide Field Planetary Camera-2 (in PC mode) aboard NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope.
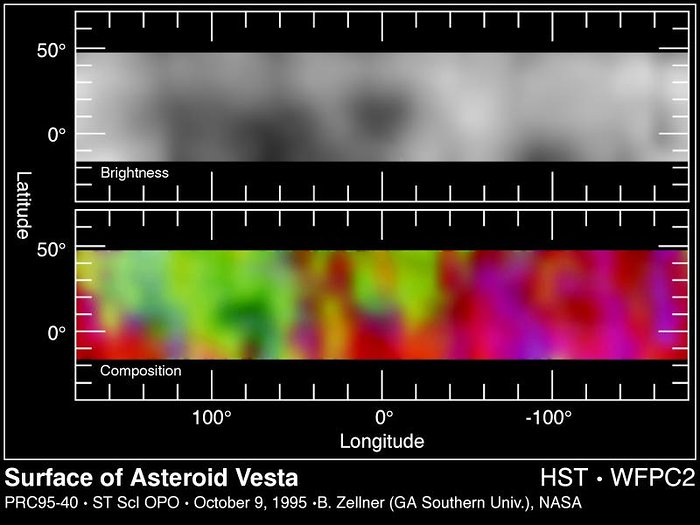
Top Image
Surface Brightness Map of Vesta - This map shows that, unlike most asteroids, Vesta's surface is significantly varied with a dark hemisphere and a light hemisphere. The surface markings may represent ancient igneous activity such as lava flows and, in addition, regions where major impacts have stripped away the crust revealing mantle material below the crust.
Bottom Image
Surface Composition Map of Vesta - This false-color composite map of Vesta results show that all of Vesta's surface is igneous, indicating that either the entire surface was once melted, or lava flowing from its interior once completely covered its surface. The map shows that Vesta has two distinct hemispheres containing two different types of solidified lava called basalts.
Credit:About the Image
About the Object
| Name: | Vesta |
| Type: | Solar System : Interplanetary Body : Asteroid |
| Category: | Solar System |
Colours & filters
| Band | Wavelength | Telescope |
|---|---|---|
| Optical B | 439 nm |
Hubble Space Telescope
WFPC2 |
| Optical R | 673 nm |
Hubble Space Telescope
WFPC2 |
| Infrared Near-IR |
Hubble Space Telescope
WFPC2 | |
| Infrared Near-IR | 1.024 μm |
Hubble Space Telescope
WFPC2 |