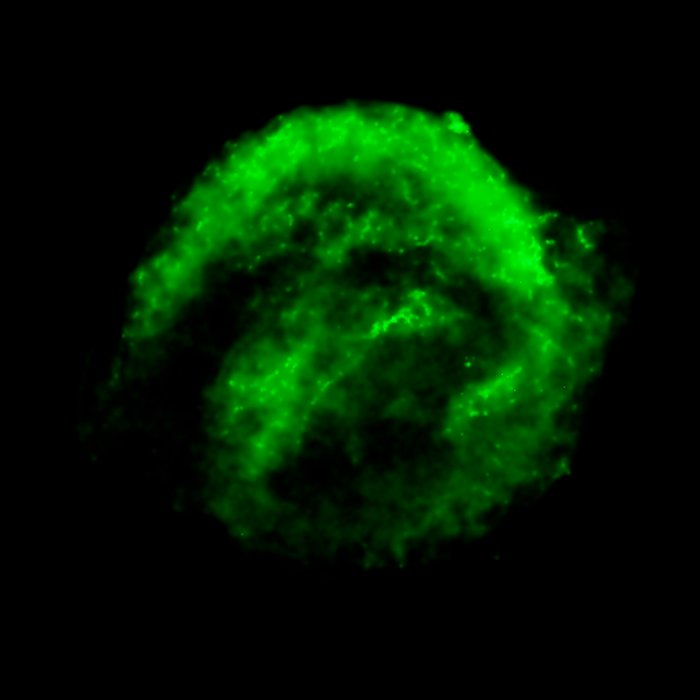
Chandra X-ray Observatory Data of Kepler's Supernova Remnant
This image shows the remains of Kepler's Supernova, the most recent exploding star to be seen in the Milky Way Galaxy. It was first observed 400 years ago when it was thought to be 'a new star'. In fact, it was the the gas and dust from an exploding star, rapidly expanding. These remnants have now reached a diameter of 14 light years wide and are still expanding at 4 million miles per hour.
This image was taken by the Chandra X-ray Observatory and shows the cooler X-ray gas which resides in a thick interior shell and marks the location of heated material expelled from the exploded star.
Credit:About the Image
About the Object
| Name: | Kepler's SN |
| Type: | Milky Way : Nebula : Type : Supernova Remnant |
| Distance: | 13000 light years |
| Constellation: | Ophiuchus |
| Category: | Nebulae |
Coordinates
| Position (RA): | 17 30 41.50 |
| Position (Dec): | -21° 29' 33.17" |
| Field of view: | 4.96 x 4.96 arcminutes |
| Orientation: | North is 0.1° left of vertical |
Colours & filters
| Band | Telescope |
|---|---|
| X-ray |
Chandra
ACIS |